Things You Need To Know About Macular Degeneration Write These Down
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a significant cause of vision loss, especially among older adults. We’ve carried out detailed research, and might help you understand the early signals of macular degeneration.
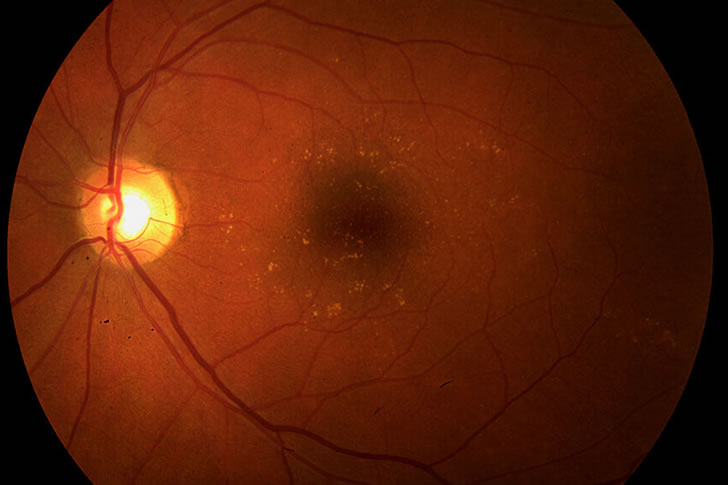
Risk Factors for Macular Degeneration
Understanding the risk factors of macular degeneration can aid in prevention and early detection. Key risk factors include:
1. Age: The likelihood of developing AMD increases significantly after age 50.
2. Genetics: Family history of AMD increases one’s risk.
3. Smoking: Smoking doubles the risk of AMD.
4. Race: Caucasians are more likely to develop AMD than African Americans or Hispanics/Latinos.
5. Diet: A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables can contribute to AMD.
Preventive measures such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet rich in green leafy vegetables and fish, and managing other health issues like hypertension and cholesterol can reduce the risk of AMD.
Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
| Symptom/Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Blurred Vision | Loss of clarity in seeing fine details, both up close and at a distance. |
| Dark or Empty Areas | Appearance of dark, blurry areas or white-out spots in the center of one’s field of vision. |
| Distorted Vision | Straight lines appear wavy or bent, common symptom that can indicate worsening of the condition. |
| Diminished Color Vision | Colors may appear less vibrant, and it can be harder to distinguish between different colors. |
| Difficulty Adapting to Low Light | Increased difficulty seeing in low light situations, such as at dusk or in dimly lit areas. |
Because AMD affects the central part of the retina but not the peripheral vision, it does not cause total blindness, but it can severely impact everyday activities like reading and driving.
Diagnosing Macular Degeneration
Early detection of macular degeneration is crucial for effective treatment. Eye exams are vital, particularly after the age of 50. During these exams, ophthalmologists may use several tests to diagnose AMD, including:
– Visual acuity tests to measure sight from various distances.
– Dilated eye exams where drops are placed to widen the pupils, allowing a better view of the retina.
– Amsler grid tests to detect central vision problems typical of macular degeneration.
Treatment and Management of AMD
While there is no cure for AMD, certain treatments and lifestyle changes can slow its progression and manage its impact on vision. Treatment options vary depending on the type of AMD.
– For Dry AMD: Treatment options are limited but often include nutritional supplements like vitamins C and E, zinc, copper, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which can sometimes slow the progression.
– For Wet AMD: Treatment can include anti-VEGF medication injections that help reduce the number of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. Laser therapy might also be used.
Regular monitoring and continued treatment under the care of an ophthalmologist can help manage AMD effectively.
Technological Aids and Living with AMD
Living with macular degeneration means adjusting to changes in vision. Various tools and devices can help maintain independence and quality of life:
– Magnifying glasses, apps, and devices: Enhanced visual aids that make everyday tasks more manageable.
– Voice recognition systems: Technological advancements that can aid in using devices without needing to read text.
– Adjusting home lighting: Brighter and more direct lighting can help reduce strain and improve clarity.
Conclusion: Facing Macular Degeneration with Awareness and Support
Although AMD presents challenges, understanding the condition and taking proactive steps can make a significant difference in managing its impact. Regular check-ups, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and utilizing available tools and support can help those affected by macular degeneration maintain an active and fulfilling life.
References
To validate the information and conclusions in this analysis, here are three credible sources:
https://www.healthline.com/health/what-are-the-early-warning-signs-of-macular-degeneration
https://patient.info/eye-care/visual-problems/age-related-macular-degeneration
https://www.visioncenter.org/conditions/macular-degeneration/







Recent Comments